Fallen Arches Explained
Overview

Fallen arches are very painful and problematic issues with feet of all ages. The easiest way to explain this medical issue that affects millions every year, is that the structural support has loosened or collapsed in the bottom of the foot. The best way to keep prevent arches from falling is to avoid them completely to begin with and there are several preventative steps that can be taken to avoid fallen arches and make sure they're not a part of your everyday life.
Causes
Footwear: shoes which limit toe movement; high heels. Barefoot walking may be protective. A tight Achilles tendon or calf muscles (heel cord contracture). This may help to cause Pes Planus, or may contribute to symptoms such as foot pain when there is existing Pes Planus. Obesity. Other bony abnormalities, eg rotational deformities, tibial abnormalities, coalition (fusion) of tarsal bones, equinus deformity. Ligamentous laxity, eg familial, Marfan's syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, Down's syndrome. Other factors causing foot pronation, eg hip abductor weakness and genu valgum.
Symptoms
Depending on the cause of the flatfoot, a patient may experience one or more of the different symptoms below. Pain along the course of the posterior tibial tendon which lies on the inside of the foot and ankle. This can be associated with swelling on the inside of the ankle. Pain that is worse with activity. High intensity or impact activities, such as running, can be very difficult. Some patients can have difficulty walking or even standing for long periods of time. When the foot collapses, the heel bone may shift position and put pressure on the outside ankle bone (fibula). This can cause pain on the outside of the ankle. Arthritis in the heel also causes this same type of pain. Patients with an old injury or arthritis in the middle of the foot can have painful, bony bumps on the top and inside of the foot. These make shoewear very difficult. Occasionally, the bony spurs are so large that they pinch the nerves which can result in numbness and tingling on the top of the foot and into the toes. Diabetics may only notice swelling or a large bump on the bottom of the foot. Because their sensation is affected, people with diabetes may not have any pain. The large bump can cause skin problems and an ulcer (a sore that does not heal) may develop if proper diabetic shoewear is not used.
Diagnosis
If your child has flatfeet, his or her doctor will ask about any family history of flatfeet or inherited foot problems. In a person of any age, the doctor will ask about occupational and recreational activities, previous foot trauma or foot surgery and the type of shoes worn. The doctor will examine your shoes to check for signs of excessive wear. Worn shoes often provide valuable clues to gait problems and poor bone alignment. The doctor will ask you to walk barefoot to evaluate the arches of the feet, to check for out-toeing and to look for other signs of poor foot mechanics. The doctor will examine your feet for foot flexibility and range of motion and feel for any tenderness or bony abnormalities. Depending on the results of this physical examination, foot X-rays may be recommended. X-rays are always performed in a young child with rigid flatfeet and in an adult with acquired flatfeet due to trauma.
best arch support insoles for plantar fasciitis
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment isn't usually needed for flat feet because the condition doesn't usually cause any significant problems. Aching feet can often be relieved by wearing supportive shoes that fit properly. You may need to wear shoes that are wider than normal. If your feet overpronate, you may need to wear a special insole (an orthotic) inside your shoes to stop your feet rolling inwards when you walk or run. These will usually need to be made and fitted by a podiatrist. Stretching your calf and Achilles tendon may also help as a tight Achilles can make your foot overpronate. To stretch your calf and Achilles tendon, step forwards with your left leg and bend it, with your right leg straight and both feet pointing forwards, push your right heel into the ground while keeping your right leg straight; you should feel the stretch at the back of your right leg, below the knee, hold the stretch for 15 to 30 seconds and repeat with the opposite leg, repeat the stretch two to four times on each leg, and repeat the overall exercise three to four times a day.
Surgical Treatment

Feet that do not respond to the treatments above may need surgery. The surgery will help to create a supportive arch.
Prevention
oll away pain. If you're feeling pain in the arch area, you can get some relief by massaging the bottom of your foot. A regular massage while you're watching TV can do wonders" Stretch out. Doing the same type of stretching exercises that runners do in their warm-up can help reduce arch pain caused by a tight heel cord. One of the best exercises is to stand about three feet from a wall and place your hands on the wall. Leaning toward the wall, bring one foot forward and bend the knee so that the calf muscles of the other leg stretch. Then switch legs. Stretching is particularly important for women who spend all week in heels and then wear exercise shoes or sneakers on weekends. Get measured each time you buy new shoes. Don't assume that since you always wore a particular size, you always will. Too many people try to squeeze into their 'regular' shoe size and wind up with serious foot problems or sores on their feet. When your arch is falling, your feet may get longer or wider and you may or may not feel pain, so getting your foot measured each time you buy shoes is a good indicator of your arch's degeneration. Examine your shoes. If the heel is worn down, replace it. But if the back portion of the shoe is distorted or bent to one side, get yourself into a new pair of supportive shoes like those made specifically for walking. That's because flat feet can affect your walking stride, and failing to replace worn shoes may lead to knee or hip pain.

Fallen arches are very painful and problematic issues with feet of all ages. The easiest way to explain this medical issue that affects millions every year, is that the structural support has loosened or collapsed in the bottom of the foot. The best way to keep prevent arches from falling is to avoid them completely to begin with and there are several preventative steps that can be taken to avoid fallen arches and make sure they're not a part of your everyday life.
Causes
Footwear: shoes which limit toe movement; high heels. Barefoot walking may be protective. A tight Achilles tendon or calf muscles (heel cord contracture). This may help to cause Pes Planus, or may contribute to symptoms such as foot pain when there is existing Pes Planus. Obesity. Other bony abnormalities, eg rotational deformities, tibial abnormalities, coalition (fusion) of tarsal bones, equinus deformity. Ligamentous laxity, eg familial, Marfan's syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, Down's syndrome. Other factors causing foot pronation, eg hip abductor weakness and genu valgum.
Symptoms
Depending on the cause of the flatfoot, a patient may experience one or more of the different symptoms below. Pain along the course of the posterior tibial tendon which lies on the inside of the foot and ankle. This can be associated with swelling on the inside of the ankle. Pain that is worse with activity. High intensity or impact activities, such as running, can be very difficult. Some patients can have difficulty walking or even standing for long periods of time. When the foot collapses, the heel bone may shift position and put pressure on the outside ankle bone (fibula). This can cause pain on the outside of the ankle. Arthritis in the heel also causes this same type of pain. Patients with an old injury or arthritis in the middle of the foot can have painful, bony bumps on the top and inside of the foot. These make shoewear very difficult. Occasionally, the bony spurs are so large that they pinch the nerves which can result in numbness and tingling on the top of the foot and into the toes. Diabetics may only notice swelling or a large bump on the bottom of the foot. Because their sensation is affected, people with diabetes may not have any pain. The large bump can cause skin problems and an ulcer (a sore that does not heal) may develop if proper diabetic shoewear is not used.
Diagnosis
If your child has flatfeet, his or her doctor will ask about any family history of flatfeet or inherited foot problems. In a person of any age, the doctor will ask about occupational and recreational activities, previous foot trauma or foot surgery and the type of shoes worn. The doctor will examine your shoes to check for signs of excessive wear. Worn shoes often provide valuable clues to gait problems and poor bone alignment. The doctor will ask you to walk barefoot to evaluate the arches of the feet, to check for out-toeing and to look for other signs of poor foot mechanics. The doctor will examine your feet for foot flexibility and range of motion and feel for any tenderness or bony abnormalities. Depending on the results of this physical examination, foot X-rays may be recommended. X-rays are always performed in a young child with rigid flatfeet and in an adult with acquired flatfeet due to trauma.
best arch support insoles for plantar fasciitis
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment isn't usually needed for flat feet because the condition doesn't usually cause any significant problems. Aching feet can often be relieved by wearing supportive shoes that fit properly. You may need to wear shoes that are wider than normal. If your feet overpronate, you may need to wear a special insole (an orthotic) inside your shoes to stop your feet rolling inwards when you walk or run. These will usually need to be made and fitted by a podiatrist. Stretching your calf and Achilles tendon may also help as a tight Achilles can make your foot overpronate. To stretch your calf and Achilles tendon, step forwards with your left leg and bend it, with your right leg straight and both feet pointing forwards, push your right heel into the ground while keeping your right leg straight; you should feel the stretch at the back of your right leg, below the knee, hold the stretch for 15 to 30 seconds and repeat with the opposite leg, repeat the stretch two to four times on each leg, and repeat the overall exercise three to four times a day.
Surgical Treatment

Feet that do not respond to the treatments above may need surgery. The surgery will help to create a supportive arch.
Prevention
oll away pain. If you're feeling pain in the arch area, you can get some relief by massaging the bottom of your foot. A regular massage while you're watching TV can do wonders" Stretch out. Doing the same type of stretching exercises that runners do in their warm-up can help reduce arch pain caused by a tight heel cord. One of the best exercises is to stand about three feet from a wall and place your hands on the wall. Leaning toward the wall, bring one foot forward and bend the knee so that the calf muscles of the other leg stretch. Then switch legs. Stretching is particularly important for women who spend all week in heels and then wear exercise shoes or sneakers on weekends. Get measured each time you buy new shoes. Don't assume that since you always wore a particular size, you always will. Too many people try to squeeze into their 'regular' shoe size and wind up with serious foot problems or sores on their feet. When your arch is falling, your feet may get longer or wider and you may or may not feel pain, so getting your foot measured each time you buy shoes is a good indicator of your arch's degeneration. Examine your shoes. If the heel is worn down, replace it. But if the back portion of the shoe is distorted or bent to one side, get yourself into a new pair of supportive shoes like those made specifically for walking. That's because flat feet can affect your walking stride, and failing to replace worn shoes may lead to knee or hip pain.
Why Is There A Leg Length Discrepancy After Hip Replacement?
Overview
Differences between the lengths of the upper and/or lower legs are called leg length discrepancies (LLD). A leg length difference may simply be a mild variation between the two sides of the body. This is not unusual in the general population. For example, one study reported that 32 percent of 600 military recruits had a 1/5 inch to a 3/5 inch difference between the lengths of their legs. This is a normal variation. Greater differences may need treatment because a significant difference can affect a patient's well-being and quality of life.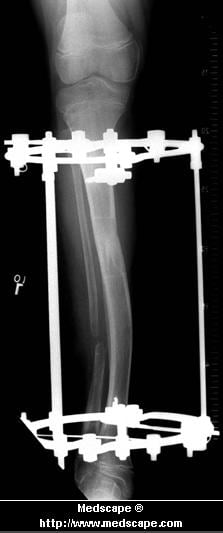
Causes
Some limb-length differences are caused by actual anatomic differences from one side to the other (referred to as structural causes). The femur is longer (or shorter) or the cartilage between the femur and tibia is thicker (or thinner) on one side. There could be actual deformities in one femur or hip joint contributing to leg length differences from side to side. Even a small structural difference can amount to significant changes in the anatomy of the limb. A past history of leg fracture, developmental hip dysplasia, slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE), short neck of the femur, or coxa vara can also lead to placement of the femoral head in the hip socket that is offset. The end-result can be a limb-length difference and early degenerative arthritis of the hip.
Symptoms
Many people walk around with LLD?s of up to 2 cm. and not even know it. However, discrepancies above 2 cm. becomes more noticeable, and a slight limp is present. But even up to 3 cm. a small lift compensates very well, and many patients are quite happy with this arrangement. Beyond 3 cm. however, the limp is quite pronounced, and medical care is often sought at that point. Walking with a short leg gait is not only unsightly, but increases energy expenditure during ambulation. It could also put more stress on the long leg, and causes functional scoliosis. Where the discrepancy is more severe, walking becomes grotesque or virtually impossible.
Diagnosis
The only way to decipher between anatomical and functional leg length inequalities (you can have both) is by a physical measurement and series of biomechanical tests. It is actually a simple process and gets to the true cause of some runner?s chronic foot, knee, hip and back pain. After the muscles are tested and the legs are measured it may be necessary to get a special X-ray that measures both of your thighs (Femurs) and legs (Tibias). The X-ray is read by a medical radiologist who provides a report of the actual difference down to the micrometer leaving zero room for error. Once the difference in leg length is known, the solution becomes clear.
Non Surgical Treatment
Whether or not treatment should be pursued depends on the amount of discrepancy. In general, no treatment (other than a heel life, if desired) should be considered for discrepancies under two centimeters. If the discrepancy measures between two and five centimeters, one might consider a procedure to equalize leg length. Usually, this would involve closure of the growth plate on the long side, thereby allowing the short side to catch up; shortening the long leg; or possibly lengthening the short leg.

how to grow tall after 18
Surgical Treatment
The type of surgery depends on the type of problem. Outpatient procedures may be used to alter the growth of the limb. This is often done through small incisions. If an outpatient procedure is done, your child can continue with most regular activities. Other times, surgery may be very involved and require the use of an external device that is attached to the limb with pins and wires. This device may be left on for months to correct the deformity or lengthen the leg. If this type of surgery is required, your child will be making weekly visits to Cincinnati Children's.
Differences between the lengths of the upper and/or lower legs are called leg length discrepancies (LLD). A leg length difference may simply be a mild variation between the two sides of the body. This is not unusual in the general population. For example, one study reported that 32 percent of 600 military recruits had a 1/5 inch to a 3/5 inch difference between the lengths of their legs. This is a normal variation. Greater differences may need treatment because a significant difference can affect a patient's well-being and quality of life.

Causes
Some limb-length differences are caused by actual anatomic differences from one side to the other (referred to as structural causes). The femur is longer (or shorter) or the cartilage between the femur and tibia is thicker (or thinner) on one side. There could be actual deformities in one femur or hip joint contributing to leg length differences from side to side. Even a small structural difference can amount to significant changes in the anatomy of the limb. A past history of leg fracture, developmental hip dysplasia, slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE), short neck of the femur, or coxa vara can also lead to placement of the femoral head in the hip socket that is offset. The end-result can be a limb-length difference and early degenerative arthritis of the hip.
Symptoms
Many people walk around with LLD?s of up to 2 cm. and not even know it. However, discrepancies above 2 cm. becomes more noticeable, and a slight limp is present. But even up to 3 cm. a small lift compensates very well, and many patients are quite happy with this arrangement. Beyond 3 cm. however, the limp is quite pronounced, and medical care is often sought at that point. Walking with a short leg gait is not only unsightly, but increases energy expenditure during ambulation. It could also put more stress on the long leg, and causes functional scoliosis. Where the discrepancy is more severe, walking becomes grotesque or virtually impossible.
Diagnosis
The only way to decipher between anatomical and functional leg length inequalities (you can have both) is by a physical measurement and series of biomechanical tests. It is actually a simple process and gets to the true cause of some runner?s chronic foot, knee, hip and back pain. After the muscles are tested and the legs are measured it may be necessary to get a special X-ray that measures both of your thighs (Femurs) and legs (Tibias). The X-ray is read by a medical radiologist who provides a report of the actual difference down to the micrometer leaving zero room for error. Once the difference in leg length is known, the solution becomes clear.
Non Surgical Treatment
Whether or not treatment should be pursued depends on the amount of discrepancy. In general, no treatment (other than a heel life, if desired) should be considered for discrepancies under two centimeters. If the discrepancy measures between two and five centimeters, one might consider a procedure to equalize leg length. Usually, this would involve closure of the growth plate on the long side, thereby allowing the short side to catch up; shortening the long leg; or possibly lengthening the short leg.

how to grow tall after 18
Surgical Treatment
The type of surgery depends on the type of problem. Outpatient procedures may be used to alter the growth of the limb. This is often done through small incisions. If an outpatient procedure is done, your child can continue with most regular activities. Other times, surgery may be very involved and require the use of an external device that is attached to the limb with pins and wires. This device may be left on for months to correct the deformity or lengthen the leg. If this type of surgery is required, your child will be making weekly visits to Cincinnati Children's.
Heel Discomfort
Overview

Pain arises in the centre of the heel and sometimes can spread to the arch region of the foot. Some patients complain of intense pain when walking the first few steps in the morning and after periods of rest. The most common cause of heel pain is plantar fascitis. The plantar fascia is a broad band of tissue that runs along the bottom of the foot. When this band of tissue is damaged due to biomechanical reasons or inappropriate running shoes then the tissue can become inflamed or even tear at the heel bone. This can be very painful.
Causes
Heel pain can have many causes but the vast majority is caused by plantar fasciitis. Plantar means, ?bottom of the foot.? Fascia is a ligament or ?bundle? of ligaments. The plantar fascia is the thick ligament that helps to hold up the foot and provide spring in our step. Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the plantar fascia and causes more than 90% of heel pain among adults in the US. Plantar fasciitis can be acute, that is, as simple strain of the ligament but often is chronic, hanging on for months if not years. Why does that happen? The answer is poor foot mechanics, the foot sinking down too far allowing the plantar fascia to overstretch with each step taken.
Symptoms
The symptoms of plantar fasciitis are classically pain of a sharp nature which is worse standing first thing in the morning. After a short period of walking the pain usually reduces or disappears, only to return again later in the day. Aggravating times are often after increased activity and rising from sitting. If these are the sort of symptoms you are experiencing then the Heel-Fix Kit ? will be just the treatment your heel is crying out for. Some heel pain is more noticeable at night and at rest. Because plantar fasciitis is a mechanical pathology it is unlikely that this sort of heel pain is caused by plantar fasciitis. The most common reason for night heel pain is pressure on your Sciatic nerve causing referred pain in the heel. Back pain is often present as well, but you can get the heel pain with little or no back pain that is caused by nerve irritation in the leg or back. If you get pain in your heels mainly or worse at night please see a clinician as soon as you can to confirm the diagnosis.
Diagnosis
In most cases, your GP or a podiatrist (a specialist in foot problems and foot care) should be able to diagnose the cause of your heel pain by asking about your symptoms and medical history, examining your heel and foot.
Non Surgical Treatment
Once diagnosed, treatment for plantar fasciitis may include one or more of the following: advice on footwear, in particular use of arch-supportive footwear; avoid walking barefoot; stretching exercises, shoe modifications such as heel pads, taping and strapping, anti-inflammatories and orthotic devices to correct abnormal foot mechanics. Injection therapy with corticosteroids is only advisable if all the conservative treatment methods mentioned above have been exhausted due to undesired effects implicated with steroid infusion in the heels.
Surgical Treatment
Only a relatively few cases of heel pain require surgery. If required, surgery is usually for the removal of a spur, but also may involve release of the plantar fascia, removal of a bursa, or a removal of a neuroma or other soft-tissue growth.
heel pain treatment
Prevention

Maintaining flexible and strong muscles in your calves, ankles, and feet can help prevent some types of heel pain. Always stretch and warm-up before exercising. Wear comfortable, properly fitting shoes with good arch support and cushioning. Make sure there is enough room for your toes.

Pain arises in the centre of the heel and sometimes can spread to the arch region of the foot. Some patients complain of intense pain when walking the first few steps in the morning and after periods of rest. The most common cause of heel pain is plantar fascitis. The plantar fascia is a broad band of tissue that runs along the bottom of the foot. When this band of tissue is damaged due to biomechanical reasons or inappropriate running shoes then the tissue can become inflamed or even tear at the heel bone. This can be very painful.
Causes
Heel pain can have many causes but the vast majority is caused by plantar fasciitis. Plantar means, ?bottom of the foot.? Fascia is a ligament or ?bundle? of ligaments. The plantar fascia is the thick ligament that helps to hold up the foot and provide spring in our step. Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the plantar fascia and causes more than 90% of heel pain among adults in the US. Plantar fasciitis can be acute, that is, as simple strain of the ligament but often is chronic, hanging on for months if not years. Why does that happen? The answer is poor foot mechanics, the foot sinking down too far allowing the plantar fascia to overstretch with each step taken.
Symptoms
The symptoms of plantar fasciitis are classically pain of a sharp nature which is worse standing first thing in the morning. After a short period of walking the pain usually reduces or disappears, only to return again later in the day. Aggravating times are often after increased activity and rising from sitting. If these are the sort of symptoms you are experiencing then the Heel-Fix Kit ? will be just the treatment your heel is crying out for. Some heel pain is more noticeable at night and at rest. Because plantar fasciitis is a mechanical pathology it is unlikely that this sort of heel pain is caused by plantar fasciitis. The most common reason for night heel pain is pressure on your Sciatic nerve causing referred pain in the heel. Back pain is often present as well, but you can get the heel pain with little or no back pain that is caused by nerve irritation in the leg or back. If you get pain in your heels mainly or worse at night please see a clinician as soon as you can to confirm the diagnosis.
Diagnosis
In most cases, your GP or a podiatrist (a specialist in foot problems and foot care) should be able to diagnose the cause of your heel pain by asking about your symptoms and medical history, examining your heel and foot.
Non Surgical Treatment
Once diagnosed, treatment for plantar fasciitis may include one or more of the following: advice on footwear, in particular use of arch-supportive footwear; avoid walking barefoot; stretching exercises, shoe modifications such as heel pads, taping and strapping, anti-inflammatories and orthotic devices to correct abnormal foot mechanics. Injection therapy with corticosteroids is only advisable if all the conservative treatment methods mentioned above have been exhausted due to undesired effects implicated with steroid infusion in the heels.
Surgical Treatment
Only a relatively few cases of heel pain require surgery. If required, surgery is usually for the removal of a spur, but also may involve release of the plantar fascia, removal of a bursa, or a removal of a neuroma or other soft-tissue growth.
heel pain treatment
Prevention

Maintaining flexible and strong muscles in your calves, ankles, and feet can help prevent some types of heel pain. Always stretch and warm-up before exercising. Wear comfortable, properly fitting shoes with good arch support and cushioning. Make sure there is enough room for your toes.
Mortons Neuroma Prevention
Overview
 Morton's neuroma is the common name given to the nerve irritation that is found in the ball of the foot that may or may not be accompanied by an inter-metatarsal bursae (a bursa-neuromal complex). It is often associated with inflammation or degeneration and often occurs with constant pressure or irritation of the nerve from the surrounding bony structures or local bursas (fluid filled sacs). Morton's Neuroma can cause symptoms such as a sharp pain, burning even a lack of feeling in the ball of the foot and associated toes.
Morton's neuroma is the common name given to the nerve irritation that is found in the ball of the foot that may or may not be accompanied by an inter-metatarsal bursae (a bursa-neuromal complex). It is often associated with inflammation or degeneration and often occurs with constant pressure or irritation of the nerve from the surrounding bony structures or local bursas (fluid filled sacs). Morton's Neuroma can cause symptoms such as a sharp pain, burning even a lack of feeling in the ball of the foot and associated toes.
Causes
The exact cause of Morton's neuroma is not known. However, it is thought to develop as a result of long-standing (chronic) stress and irritation of a plantar digital nerve. There are a number of things that are thought to contribute to this. Some thickening (fibrosis) and swelling may then develop around a part of the nerve. This can look like a neuroma and can lead to compression of the nerve. Sometimes, other problems can contribute to the compression of the nerve. These include the growth of a fatty lump (called a lipoma) and also the formation of a fluid-filled sac that can form around a joint (a bursa). Also, inflammation in the joints in the foot next to one of the digital nerves can sometimes cause irritation of the nerve and lead to the symptoms of Morton's neuroma.
Symptoms
Neuroma pain is classically described as a burning pain in the forefoot. It can also be felt as an aching or shooting pain in the forefoot. Patients with this problem frequently say they feel like they want to take off their shoes and rub their foot. This pain may occur in the middle of a run or at the end of a long run. If your shoes are quite tight or the neuroma is very large, the pain may be present even when walking. Occasionally a sensation of numbness is felt in addition to the pain or even before the pain appears.
Diagnosis
Podiatrists conduct a physical examination and may order imaging tests, such as x-ray or MRI scan to diagnose Morton's neuroma. Conservative treatment options include custom-fitted orthotics, medication, and/or alcohol injections designed to harden the nerve. However, most patients with Morton's neuroma need minor surgery.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment options vary with the severity of each neuroma, and identifying the neuroma early in its development is important to avoid surgical correction. For simple, undeveloped neuromas, a pair of thick-soled shoes with a wide toe box is often adequate treatment to relieve symptoms, allowing the condition to diminish on its own. For more severe conditions, however, additional treatment or surgery may be necessary to remove the tumor. The primary goal of most early treatment regimens is to relieve pressure on areas where a neuroma develops. Your podiatric physician will examine and likely X-ray the affected area and suggest a treatment plan that best suits your individual case. Padding and Taping. Special padding at the ball of the foot may change the abnormal foot function and relieve the symptoms caused by the neuroma. Medication. Anti-inflammatory drugs and cortisone injections can be prescribed to ease acute pain and inflammation caused by the neuroma. Orthotics. Custom shoe inserts made by your podiatrist may be useful in controlling foot function. Orthotics may reduce symptoms and prevent the worsening of the condition.
Surgical Treatment
The ultimate success of a Morton?s neuroma treated surgically is somewhat unclear. This is likely due to the idea that in most instances a ?Morton?s neuroma? is actually more than just an isolated nerve problem but rather consitutes a metatarsalgia where other structures (such a as the MTP joints) are also problematic, not just the nerve. Therefore, addressing the nerve as well as the other components of a metatarsalgia may offer a better chance of surgical success. However, like many conditions in foot and ankle, it is ideal if this condition can be managed without surgery.
 Morton's neuroma is the common name given to the nerve irritation that is found in the ball of the foot that may or may not be accompanied by an inter-metatarsal bursae (a bursa-neuromal complex). It is often associated with inflammation or degeneration and often occurs with constant pressure or irritation of the nerve from the surrounding bony structures or local bursas (fluid filled sacs). Morton's Neuroma can cause symptoms such as a sharp pain, burning even a lack of feeling in the ball of the foot and associated toes.
Morton's neuroma is the common name given to the nerve irritation that is found in the ball of the foot that may or may not be accompanied by an inter-metatarsal bursae (a bursa-neuromal complex). It is often associated with inflammation or degeneration and often occurs with constant pressure or irritation of the nerve from the surrounding bony structures or local bursas (fluid filled sacs). Morton's Neuroma can cause symptoms such as a sharp pain, burning even a lack of feeling in the ball of the foot and associated toes.Causes
The exact cause of Morton's neuroma is not known. However, it is thought to develop as a result of long-standing (chronic) stress and irritation of a plantar digital nerve. There are a number of things that are thought to contribute to this. Some thickening (fibrosis) and swelling may then develop around a part of the nerve. This can look like a neuroma and can lead to compression of the nerve. Sometimes, other problems can contribute to the compression of the nerve. These include the growth of a fatty lump (called a lipoma) and also the formation of a fluid-filled sac that can form around a joint (a bursa). Also, inflammation in the joints in the foot next to one of the digital nerves can sometimes cause irritation of the nerve and lead to the symptoms of Morton's neuroma.
Symptoms
Neuroma pain is classically described as a burning pain in the forefoot. It can also be felt as an aching or shooting pain in the forefoot. Patients with this problem frequently say they feel like they want to take off their shoes and rub their foot. This pain may occur in the middle of a run or at the end of a long run. If your shoes are quite tight or the neuroma is very large, the pain may be present even when walking. Occasionally a sensation of numbness is felt in addition to the pain or even before the pain appears.
Diagnosis
Podiatrists conduct a physical examination and may order imaging tests, such as x-ray or MRI scan to diagnose Morton's neuroma. Conservative treatment options include custom-fitted orthotics, medication, and/or alcohol injections designed to harden the nerve. However, most patients with Morton's neuroma need minor surgery.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment options vary with the severity of each neuroma, and identifying the neuroma early in its development is important to avoid surgical correction. For simple, undeveloped neuromas, a pair of thick-soled shoes with a wide toe box is often adequate treatment to relieve symptoms, allowing the condition to diminish on its own. For more severe conditions, however, additional treatment or surgery may be necessary to remove the tumor. The primary goal of most early treatment regimens is to relieve pressure on areas where a neuroma develops. Your podiatric physician will examine and likely X-ray the affected area and suggest a treatment plan that best suits your individual case. Padding and Taping. Special padding at the ball of the foot may change the abnormal foot function and relieve the symptoms caused by the neuroma. Medication. Anti-inflammatory drugs and cortisone injections can be prescribed to ease acute pain and inflammation caused by the neuroma. Orthotics. Custom shoe inserts made by your podiatrist may be useful in controlling foot function. Orthotics may reduce symptoms and prevent the worsening of the condition.

Surgical Treatment
The ultimate success of a Morton?s neuroma treated surgically is somewhat unclear. This is likely due to the idea that in most instances a ?Morton?s neuroma? is actually more than just an isolated nerve problem but rather consitutes a metatarsalgia where other structures (such a as the MTP joints) are also problematic, not just the nerve. Therefore, addressing the nerve as well as the other components of a metatarsalgia may offer a better chance of surgical success. However, like many conditions in foot and ankle, it is ideal if this condition can be managed without surgery.
The Solution To Leg Length Difference Are Shoe Lifts
There are not one but two different kinds of leg length discrepancies, congenital and acquired. Congenital means you are born with it. One leg is anatomically shorter than the other. As a result of developmental phases of aging, the human brain senses the walking pattern and recognizes some variance. The human body usually adapts by dipping one shoulder to the "short" side. A difference of less than a quarter inch is not blatantly irregular, demand Shoe Lifts to compensate and normally won't have a serious effect over a lifetime.

Leg length inequality goes typically undiagnosed on a daily basis, however this condition is easily corrected, and can eliminate quite a few incidents of back pain.
Therapy for leg length inequality commonly involves Shoe Lifts . They are economical, normally being under twenty dollars, in comparison to a custom orthotic of $200 or maybe more. Differences over a quarter inch can take their toll on the spine and should probably be compensated for with a heel lift. In some cases, the shortage can be so extreme that it requires a full lift to both the heel and sole of the shoe.
Lumbar pain is the most common ailment impacting people today. Over 80 million men and women have problems with back pain at some stage in their life. It's a problem which costs businesses millions year after year as a result of time lost and production. Fresh and superior treatment methods are constantly sought after in the hope of reducing the economical influence this condition causes.

People from all corners of the world suffer the pain of foot ache as a result of leg length discrepancy. In most of these situations Shoe Lifts can be of very helpful. The lifts are capable of reducing any discomfort in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by many professional orthopaedic physicians.
So as to support the human body in a well-balanced manner, the feet have a critical role to play. Irrespective of that, it's often the most neglected zone of the body. Many people have flat-feet which means there is unequal force placed on the feet. This will cause other body parts such as knees, ankles and backs to be impacted too. Shoe Lifts make sure that the right posture and balance are restored.

Leg length inequality goes typically undiagnosed on a daily basis, however this condition is easily corrected, and can eliminate quite a few incidents of back pain.
Therapy for leg length inequality commonly involves Shoe Lifts . They are economical, normally being under twenty dollars, in comparison to a custom orthotic of $200 or maybe more. Differences over a quarter inch can take their toll on the spine and should probably be compensated for with a heel lift. In some cases, the shortage can be so extreme that it requires a full lift to both the heel and sole of the shoe.
Lumbar pain is the most common ailment impacting people today. Over 80 million men and women have problems with back pain at some stage in their life. It's a problem which costs businesses millions year after year as a result of time lost and production. Fresh and superior treatment methods are constantly sought after in the hope of reducing the economical influence this condition causes.

People from all corners of the world suffer the pain of foot ache as a result of leg length discrepancy. In most of these situations Shoe Lifts can be of very helpful. The lifts are capable of reducing any discomfort in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by many professional orthopaedic physicians.
So as to support the human body in a well-balanced manner, the feet have a critical role to play. Irrespective of that, it's often the most neglected zone of the body. Many people have flat-feet which means there is unequal force placed on the feet. This will cause other body parts such as knees, ankles and backs to be impacted too. Shoe Lifts make sure that the right posture and balance are restored.
What Are The Major Causes Of Inferior Calcaneal Spur

Overview
Heel spurs are a common reason for people to visit their podiatrist serving Scottsdale. These small calcium deposits can cause major pain, but treatments are available to relieve your symptoms. Heel spurs grow along the plantar fascia and create a sensation similar to that of a pebble being stuck in your shoe. Your podiatrist will use a physical exam plus X-rays to determine if a heel spur is the cause of your foot pain before beginning treatment. If you do have a heel spur, your podiatrist may recommend a cortisone injection to ease inflammation. Other techniques, such as stretching the calf muscles, treating the heel with ice, and wearing a custom orthotic may also provide relief from the discomfort of a heel spur.
Causes
The plantar fascia is a big strong ligament on the bottom of the foot, starting at the bottom of the heel bone and running into the ball of the foot. As the arch of the foot becomes weak, it sags slightly with each step and this causes the plantar fascia to tug and pull at the heel bone with each step. Over a period of time, a spur forms where this big strong ligament tugs and pulls at the heel bone. Soon, inflammation (swelling) starts around this spur and the pain becomes almost unbearable. (Sometimes heel spurs may be present without being painful if no inflammation is present).

Symptoms
Most people think that a bone "spur" is sharp and produces pain by pressing on tissue, when in fact, these bony growths are usually smooth and flat. Although they rarely cause pain on their own, bone spurs in the feet can lead to callus formation as tissue builds up to provide added cushion over the area of stress. Over time, wear and tear on joints may cause these spurs to compress neighboring ligaments, tendons or nerves, thus injuring tissue and causing swelling, pain and tearing.
Diagnosis
A thorough history and physical exam is always necessary for the proper diagnosis of heel spurs and other foot conditions. X rays of the heel area are helpful, as excess bone production will be visible.
Non Surgical Treatment
The key for the proper treatment of heel spurs is determining what is causing the excessive stretching of the plantar fascia. When the cause is over-pronation (flat feet), an orthotic with rearfoot posting and longitudinal arch support is an effective device to reduce the over-pronation, and allow the condition to heal. Other common treatments include stretching exercises, losing weight, wearing shoes that have a cushioned heel that absorbs shock, and elevating the heel with the use of a heel cradle, heel cup, or orthotic. Heel cradles and heel cups provide extra comfort and cushion to the heel, and reduce the amount of shock and shear forces experienced from everyday activities.
Surgical Treatment
In a small number of cases (usually less than 5 percent), patients may not experience relief after trying the recommendations listed above. It is important that conservative treatments (such as those listed above) be performed for AT LEAST a year before considering surgery. Time is important in curing the pain from heel spurs, and insufficient treatment before surgery may subject you to potential complications from the procedure. If these treatments fail, your doctor may consider an operation to loosen the plantar fascia, called a plantar fascia release.
What Is A Calcaneal Spur

Overview
Heel spurs (calcaneal spurs) are protrusions (bumps) on the forward underside of the heel bone that can occur when the plantar tendon pulls excessively in the area where it attaches to the bone. The condition is often associated with plantar fasciitis, although it can also occur on its own. Heel spurs typically are not painful unless they intrude into the soft tissue (plantar fascia), where they can cause irritation that results in heel pain.
Causes
You are more likely to develop plantar fasciitis and heel spurs if you are Active. Sports that place excessive stress on the heel bone and attached tissue, especially if you have tight calf muscles or a stiff ankle from a previous ankle sprain, which limits ankle movement eg. running, ballet dancing and aerobics. Overweight. Carrying around extra weight increases the strain and stress on your plantar fascia. Pregnant. The weight gain and swelling associated with pregnancy can cause ligaments to become more relaxed, which can lead to mechanical problems and inflammation. On your feet. Having a job that requires a lot of walking or standing on hard surfaces ie factory workers, teachers and waitresses. Flat Feet or High Foot Arches. Changes in the arch of your foot changes the shock absorption ability and can stretch and strain the plantar fascia, which then has to absorb the additional force. Middle-Aged or Older. With ageing the arch of your foot may begin to sag - putting extra stress on the plantar fascia. Wearing shoes with poor support. Weak Foot Arch Muscles. Muscle fatigue allows your plantar fascia to overstress and cause injury. Arthritis. Some types of arthritis can cause inflammation in the tendons in the bottom of your foot, which may lead to plantar fasciitis. Diabetes. Although doctors don't know why, plantar fasciitis occurs more often in people with diabetes.

Symptoms
Heel spurs often cause no symptoms. But heel spurs can be associated with intermittent or chronic pain, especially while walking, jogging, or running, if inflammation develops at the point of the spur formation. In general, the cause of the pain is not the heel spur itself but the soft-tissue injury associated with it. Many people describe the pain of heel spurs and plantar fasciitis as a knife or pin sticking into the bottom of their feet when they first stand up in the morning, a pain that later turns into a dull ache. They often complain that the sharp pain returns after they stand up after sitting for a prolonged period of time.
Diagnosis
A heel spur is often seen on X-ray as a bony protrusion, which can vary in size. However, because a Heel Spur only indicates increased load on the plantar fascia, and not pain, an ultra sound may be required to assess other actual cause of the heel pain such and may include checking to see if the plantar fascia is inflamed or degenerated.
Non Surgical Treatment
Acupuncture and acupressure can used to address the pain of heel spurs, in addition to using friction massage to help break up scar tissue and delay the onset of bony formations. Physical therapy may help relieve pain and improve movement. The Feldenkrais method could be especially helpful for retraining some of the compensation movements caused by the pain from the spur. Guided imagery or a light massage on the foot may help to relieve some of the pain. Other treatments include low-gear cycling, and pool running. Some chiropractors approve of moderate use of aspirin or ibuprofen, or other appropriate anti-inflammatory drugs. Chiropractic manipulation is not recommended, although chiropractors may offer custom-fitted shoe orthotics and other allopathic-type treatments.
Surgical Treatment
When chronic heel pain fails to respond to conservative treatment, surgical treatment may be necessary. Heel surgery can provide relief of pain and restore mobility. The type of procedure used is based on examination and usually consists of releasing the excessive tightness of the plantar fascia, called a plantar fascia release. Depending on the presence of excess bony build up, the procedure may or may not include removal of heel spurs. Similar to other surgical interventions, there are various modifications and surgical enhancements regarding surgery of the heel.
Prevention
Heel Spur symptoms can be prevented from returning by wearing proper shoes and using customized orthotics and insoles to relieve pressure. It is important to perform your exercises to help keep your foot stretched and relaxed.